A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that occurs in any part of the urinary system. This system includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. In the context of bladder infection vs UTI, it is essential to understand that UTIs come in different forms.
There are two main types of UTIs: upper and lower. Upper UTIs affect the kidneys and ureters, often leading to more severe symptoms like fever and back pain. Lower UTIs impact the bladder and urethra, causing discomfort during urination and frequent urges to urinate.
The most common cause of UTIs is bacteria, particularly Escherichia coli (E. coli), which naturally resides in the digestive tract. Poor hygiene, dehydration, or holding in urine for too long can increase the risk of a UTI. Understanding these causes helps in managing and preventing infections effectively.
What Is a Bladder Infection?
A bladder infection, medically referred to as cystitis, is a specific condition that primarily affects the bladder. When discussing bladder infections vs. UTIs, it’s important to note that a bladder infection is a common type of urinary tract infection. It often causes pelvic pain, frequent urges to urinate, and discomfort during urination.
Bladder infections are common, particularly among women, with 50% to 60% experiencing at least one UTI in their lifetime, according to the NIH. However, some individuals are more prone to recurring infections.
This condition falls under the broader UTI umbrella because it targets the lower part of the urinary system. Unlike upper UTIs that affect the kidneys, bladder infections are typically less severe but still require prompt attention.
Various factors contribute to bladder infections. Poor hygiene habits can introduce harmful bacteria into the urethra. Certain medications may disrupt the bladder’s natural defense mechanisms, making it vulnerable. Sexual activity also increases the risk, as it facilitates the transfer of bacteria to the urinary tract. Taking proactive steps can help lower the chances of developing this type of infection.
Symptoms: Comparing Bladder Infections and UTIs
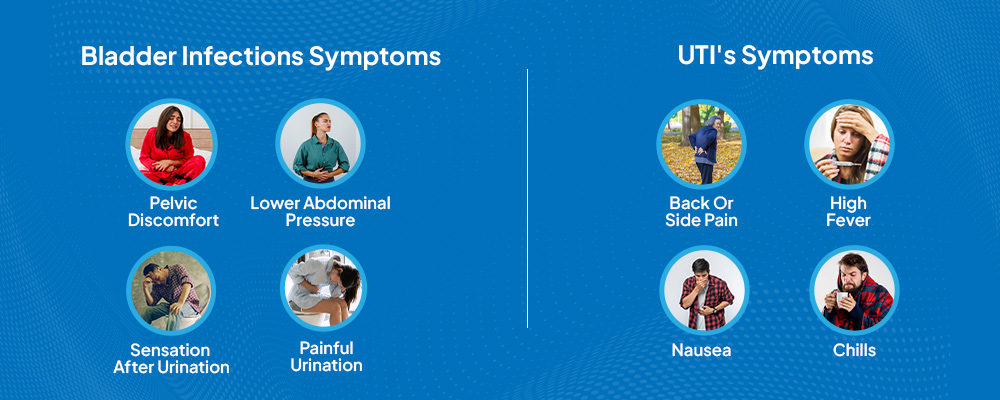
Understanding the Symptoms of Bladder Infection vs. UTI
Both conditions share several noticeable signs, including painful urination, an urgent need to urinate, and frequent trips to the bathroom. These shared symptoms often make it challenging to distinguish between the two.
Symptoms of Bladder Infection:
Bladder infections, however, come with specific symptoms, including:
- Pelvic discomfort
- Lower abdominal pressure
- Sensation of incomplete emptying after urination
- Painful urination
- Frequent urge to urinate
In contrast, severe or upper UTIs, which involve the kidneys, present with more alarming symptoms, such as:
- Back or side pain
- High fever
- Nausea
- Chills
Recognizing these differences is crucial to determining the type and severity of the infection, ensuring timely treatment.
Causes and Risk Factors
When comparing bladder infection vs UTI, exploring their causes and risk factors provides valuable insight.
- Both conditions often result from bacterial infections, with E. coli being a primary culprit.
- Factors like poor hydration, holding in urine, and improper hygiene increase the likelihood of developing these infections.
- Bladder infections have unique risk factors. For example, the female anatomy, with its shorter urethra, allows bacteria easier access to the bladder.
- Additional risks include health conditions like kidney stones or the use of urinary catheters.
- Chronic health issues such as diabetes or a weakened immune system also play a significant role.
- Diabetes can impair bladder function, while a compromised immune system makes fighting infections more difficult.
Recognizing these factors helps in reducing the chances of recurrent infections and improving urinary health.
Diagnosis and Tests
Accurate diagnosis is vital when evaluating bladder infection. Doctors often begin with a urine test to detect bacteria or blood. This test identifies signs of infection and determines whether antibiotics are necessary. Along with the urine test, a physical exam helps assess symptoms and rule out other conditions.
In some cases, further testing may become necessary. Imaging tests like ultrasounds or CT scans help detect structural issues or blockages in the urinary tract. For recurring infections, a cystoscopy allows doctors to examine the bladder directly.
Pinpointing the infection’s exact location in the urinary system ensures the right treatment plan. Addressing the problem promptly reduces the risk of complications or severe symptoms.
Treatment Options
When it comes to bladder infection vs UTI, treatment often overlaps but varies depending on the infection’s severity and location.
- Doctors typically prescribe antibiotics to eliminate bacteria, which is the primary cause of both conditions. Staying well-hydrated helps flush out bacteria from the urinary tract and supports faster recovery.
- In addition to medical treatments, home remedies can provide relief and aid prevention. Cranberry supplements or juice may reduce bacteria’s ability to stick to the bladder walls.
- Practicing proper hygiene, such as wiping front to back, lowers the risk of future infections.
- For individuals with recurrent infections, lifestyle changes can make a significant difference.
- Drinking plenty of water daily and avoiding irritants like caffeine or spicy foods promote better urinary health.
Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider ensure effective management and prevention of recurring problems.
Shape the Future of UTI Treatment by Joining Clinical Trials
Uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common but can become challenging to treat, especially when caused by drug-resistant E. coli. Clinical trials in Oklahoma City, OK, are actively seeking participants to explore innovative treatment options for these infections. By joining these trials, participants can contribute to groundbreaking research aimed at addressing resistance to current antibiotics while potentially gaining access to advanced therapies. These studies play a crucial role in improving UTI management, benefiting not only those affected today but also paving the way for better treatments in the future.
Prevention Tips
Preventing bladder infection or UTI requires consistent efforts and mindful habits to maintain a healthy urinary system. Proper hygiene practices significantly reduce the risk of infections.
For women and people with vulvas, always wipe from front to back after using the bathroom. This keeps bacteria from stool away from the urethra, reducing the risk of infection.
Regularly changing sanitary products during menstruation further minimizes bacterial growth.
Staying hydrated is another essential step. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day helps flush bacteria from the urinary system. Avoid holding in urine for long periods, as it increases the likelihood of bacterial buildup.
For individuals prone to recurrent infections, proactive measures are crucial. Consider urinating before and after sexual activity to clear bacteria from the urethra.
Incorporating cranberry supplements or vitamin C into your routine may support urinary health. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help manage underlying issues contributing to frequent infections.
Advancing UTI Care: Join Hightower Clinical Institute’s Study on Simple UTIs
Hightower Clinical is conducting a study on uncomplicated UTIs to explore advanced treatment options. Participants in the study may gain access to innovative therapies, expert medical care, and contribute to enhancing the understanding of UTI management. This research aims to improve treatment outcomes and develop better prevention strategies. Join us in shaping the future of UTI care!
Conclusion:
Understanding the differences between bladder infection vs UTI helps in identifying symptoms, managing causes, and seeking appropriate treatment. While both conditions result from bacterial infections, bladder infections are a type of UTI and often present symptoms, such as pelvic discomfort. Preventive measures, including proper hygiene, hydration, and lifestyle adjustments, play a key role in reducing infection risks. Prompt diagnosis and treatment ensure faster recovery and prevent complications. For those prone to recurrent infections, regular healthcare consultations and proactive strategies are essential for maintaining urinary health.





